Original Source: http://feedproxy.google.com/~r/tympanus/~3/Y4bYyA4e2OY/

Applying texture to text is one of the most popular text effects in graphic design. As much of print and graphic design has made its way into the Web platform, such effects have also been recreated on the Web using CSS, as well as using features of SVG such as patterns, masks and clipping paths. I have an article right here on Codrops that gives you a full overview of different ways to create textured text on the Web using CSS and SVG today that you may be interested in checking out. Yoksel touched on another area of this topic and wrote an article all about animating text fills.
However, one effect that was untouched on was that of text conforming to the texture of a surface. When text conforms to a surface, it takes the shape of that surface. Depending on the surface and texture used, you could end up some really eye-catching results. This is what this article will touch on. And the best part? All these effects are applied to real, searchable, selectable and accessible text.
This is the fifth in a series of articles on SVG filters. In the previous weeks, we got an introduction to SVG filters and learned how to create and use them to produce various effects from outlined text to posterized images, and how to replicate Photoshop-like duotone image effects with SVG filter operations.
Conforming Text to Surface Texture: The Photoshop Way
As with the duotone effect, I looked into how to make text conform to surface texture in Photoshop in an attempt to replicate that effect with SVG filters. I found this step-by-step tutorial on YouTube. The following video is a sped-up version of that tutorial:
In the Photoshop tutorial, the designer created this effect by using what is known as a displacement map. A displacement map is an image whose color information is used to distort the content of another element. To create our text effect, the texture of the image will be used to distort the text so that it conforms to the shape of the texture.
In Photoshop, in order to conform text to a surface the designer followed these steps:
Desaturate the image.
Reduce the amount of detail in the image by blurring it by 1px.
Save the image as a displacement map.
Create the text, and apply a distortion filter to it using the image as a displacement map.
Re-use the original image as a background behind the text.
Then refine the effect more by adding a slight transparency to the text and blending it with the background image.
The displacement map image is blurred in the second step before it is used to displace the text because if the image has too much or too little detail the resulting effect would look less realistic. Usually blurring the image up to 2px is enough to get a moderate amount of detail that’s just enough.
If you’ve read the previous articles in this series, you know that thinking in steps is important to create and recreate effects with SVG filter primitives. And you may have already guessed how to replicate some of these steps using SVG filter primitives, a few of which we have covered in the previous articles.
But the most important step in this effect is the creation and application of the displacement map. How do we do that in SVG?
Conforming Text to Surface Texture in SVG
In order to recreate the effect from the Photoshop tutorial above, we need to first create a displacement map. In SVG, the feDisplacementMap primitive is used to displace content using a displacement map.
feDisplacementMap takes two inputs to produce one result. The image you want to use to displace your content is specified in the in2 attribute. The in attribute is reserved for the input that you want to apply the displacement effect to.
And as with all other primitives, the input for feDisplacementMap can be anything from the SourceGraphic itself to the result of another filter operation. And since we want to apply the displacement map to our source text, this means that the in attribute will have SourceGraphic for a value.
So let’s recreate the Photoshop tutorial steps with SVG filter primitives. The process of conforming text to texture in SVG is very similar to that we saw in Photoshop. I’ll elaborate on each step as we go.
Get the image that will be used as a texture using feImage.
Desaturate the image using feColorMatrix.
Apply a 0.5px Gaussian blur to the image using feGaussianBlur.
Use the image to distort the text using feDisplacementMap.
Blend the text into the background image using feBlend and apply a translucent effect to it (decrease opacity using feComponentTransfer).
Display the text and the image behind it by merging the two layers using feMerge.
The feImage filter primitive is the filter version of the <image> element and has the same attributes as the <image> element too. So in order to render an image in the filter region, we will use feImage. Once we’ve got our image, we can use it as input to other filter operations. It will be used by the feColorMatrix operation to boot because we need to desaturate it.
We’ve mentioned feColorMatrix before, but what we didn’t mention is it comes with a few keywords that are shortcuts to pre-defined matrices. Instead of always having to provide a matrix as a value, you can change the type attribute and use one of the keywords available:
matrix | saturate | hueRotate | luminanceToAlpha
The matrix type is what you’d use when you want to provide a custom matrix as a value for the matrix operation. The other keywords are convenience shortcuts.
To desaturate an image, we use the saturate type. You specify the amount by which you want to desaturate the image in the values attribute. Since we want to completely desaturate our image, we will provide 0 as a value. Note that values are provided as fractions, with 1 (default value) being fully saturated and 0 being completely desaturated (grayscale).
So, let’s start translating our steps into code:
<!– I’m extending the filter region just to increase its area for visual purposes. This is not required or needed for the effect to work.–>
<filter id=”conform” x=”-50%” y=”-50%” width=”200%” height=”200%”>
<!– Get the image. –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none”></feImage>
<!– Desaturate the image. –>
<feColorMatrix type=”saturate” values=”0″ result=”IMAGE”/>
<!– … –>
At this point, our filter region looks like this:

After desaturating the image, we will blur it by a small amount enough to reduce the amount of detail without losing too much of it. For this particular effect, I chose to blur it by 0.25 pixels only. You may need to experiment with the values to get the right one depending on the image you use and the effect you’re after.
<!– I’m extending the filter region just to increase its area for visual purposes. This is not required or needed for the effect to work.–>
<filter id=”conform” x=”-50%” y=”-50%” width=”200%” height=”200%”>
<!– Get the image. –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none”></feImage>
<!– Desaturate the image. –>
<feColorMatrix type=”saturate” values=”0″ result=”IMAGE”/>
<!– decrease level of details so the effect on text is more realistic –>
<feGaussianBlur in=”IMAGE” stdDeviation=”0.25″ result=”MAP”></feGaussianBlur>
<!– … –>
And our displacement map now looks like this:

Using feDisplacementMap we can now distort the text with our displacement map:
<!– I’m extending the filter region just to increase its area for visual purposes. This is not required or needed for the effect to work.–>
<filter id=”conform” x=”-50%” y=”-50%” width=”200%” height=”200%”>
<!– Get the image. –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none”></feImage>
<!– Desaturate the image. –>
<feColorMatrix type=”saturate” values=”0″ result=”IMAGE”/>
<!– decrease level of details so the effect on text is more realistic –>
<feGaussianBlur in=”IMAGE” stdDeviation=”0.25″ result=”MAP”></feGaussianBlur>
<!– Use the displacement map to distort the source text –>
<feDisplacementMap in=”SourceGraphic” in2=”MAP” scale=”15″ xChannelSelector=”R” yChannelSelector=”R” result=”TEXTURED_TEXT”></feDisplacementMap>
<!– … –>
At this point, the image we used to distort the text is no longer rendered as it has been used to generate a new result, which is the distorted text. The filter region at this point thus only contains the text that is now conforming to the shape and texture of the fabric in our displacement map:

You can already see the texture of the fabric take shape on the edges of the text. This is great.
Just like in the Photoshop tutorial, we will now re-display the image behind the text. We will do that by using feImage again:
<!– I’m extending the filter region just to increase its area for visual purposes. This is not required or needed for the effect to work.–>
<filter id=”conform” x=”-50%” y=”-50%” width=”200%” height=”200%”>
<!– Get the image. –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none”></feImage>
<!– Desaturate the image. –>
<feColorMatrix type=”saturate” values=”0″ result=”IMAGE”/>
<!– decrease level of details so the effect on text is more realistic –>
<feGaussianBlur in=”IMAGE” stdDeviation=”0.25″ result=”MAP”></feGaussianBlur>
<!– Use the displacement map to distort the source text –>
<feDisplacementMap in=”SourceGraphic” in2=”MAP” scale=”15″ xChannelSelector=”R” yChannelSelector=”R” result=”TEXTURED_TEXT”></feDisplacementMap>
<!– Re-display the image as a background image –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none” result=”BG”></feImage>
<!– … –>
Lastly, we want to blend the text into the background image to improve the effect. We will decrease the opacity of the text to 0.9 using feColorMatrix, and then we will use the feBlend primitive to apply a blending mode to the text.
Similar to CSS Blend Modes, we have 16 blend modes to choose from. For our effect, the multiply blend mode will do. (In the Photoshop tutorial, the designer used the linear burn, which is not available in SVG/CSS.)
feBlend will take two inputs to blend together: the text and the background image:
<!– I’m extending the filter region just to increase its area for visual purposes. This is not required or needed for the effect to work.–>
<filter id=”conform” x=”-50%” y=”-50%” width=”200%” height=”200%”>
<!– Get the image. –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none”></feImage>
<!– Desaturate the image. –>
<feColorMatrix type=”saturate” values=”0″ result=”IMAGE”/>
<feGaussianBlur in=”IMAGE” stdDeviation=”0.25″ result=”MAP”></feGaussianBlur>
<!– Use the displacement map to distort the source text –>
<feDisplacementMap in=”SourceGraphic” in2=”MAP” scale=”15″ xChannelSelector=”R” yChannelSelector=”R” result=”TEXTURED_TEXT”></feDisplacementMap>
<!—->
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none” result=”BG”></feImage>
<!– Reduce the opacity of the text –>
<feColorMatrix in=”Textured_Text” result=”Textured_Text_2″ type=”matrix”
values=”1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 .9 0″ />
<!– Blend the text with the background –>
<feBlend in=”BG” in2=”Textured_Text_2″ mode=”multiply” result=”BLENDED_TEXT”></feBlend>
<!– … –>
And last by not least, we will layer the new blended text layer on top of the background image layer with feMerge:
<!– I’m extending the filter region just to increase its area for visual purposes. This is not required or needed for the effect to work.–>
<filter id=”conform” x=”-50%” y=”-50%” width=”200%” height=”200%”>
<!– Get the image. –>
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none”></feImage>
<!– Desaturate the image. –>
<feColorMatrix type=”saturate” values=”0″ result=”IMAGE”/>
<!– decrease level of details so the effect on text is more realistic –>
<feGaussianBlur in=”IMAGE” stdDeviation=”0.25″ result=”MAP”></feGaussianBlur>
<!– Use the displacement map to distort the source text –>
<feDisplacementMap in=”SourceGraphic” in2=”MAP” scale=”15″ xChannelSelector=”R” yChannelSelector=”R” result=”TEXTURED_TEXT”></feDisplacementMap>
<!—->
<feImage xlink:href=”…” x=”0″ y=”0″ width=”100%” height=”100%” preserveAspectRatio=”none” result=”BG”></feImage>
<!– Reduce the opacity of the text –>
<feColorMatrix in=”Textured_Text” result=”Textured_Text_2″ type=”matrix”
values=”1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 .9 0″ />
<!– Blend the text with the background –>
<feBlend in=”BG” in2=”Textured_Text_2″ mode=”multiply” result=”BLENDED_TEXT”></feBlend>
<!– Layer the text on top of the background image –>
<feMerge>
<feMergeNode in=”BG”></feMergeNode>
<feMergeNode in=”BLENDED_TEXT”></feMergeNode>
</feMerge>
</filter>
<text dx=”60″ dy=”200″ font-size=”10em” font-weight=”bold” filter=”url(#conform)” fill=”#00826C”> organic </text>
And this is our final result:

Notes about using Displacement Maps in SVG
The feDisplacementMap element has three attributes that determine how the displacement map will affect the source graphic:
xChannelSelector: specifies which color channel (R/G/B/A) from in2 to use for the horizontal displacement;
yChannelSelector: specifies which color channel (R/G/B/A) from in2 to use for the vertical displacement;
scale: determines the amount by which you want to distort the image. The higher the scale, the stronger the distortion effect is. You’ll probably find yourself experimenting with this value to get the desired result.
Possibly the most important thing to be aware of when using images to displace content in SVG filters is that the image and the content are subject to CORS rules. Make sure you’re serving both the image and the content from the same source to ensure that the browser does not skip the displacement operation.
You can also inline an image in the filter (in feImage) and use it as a displacement map. This pen by Gabi is a great example which uses an inlined SVG pattern to distort the source image. The circular pattern resulting in a ripple-like effect is my favorite.
Applying a Transformation to the Source Text
In the Photoshop tutorial that we followed for this effect, the designer applies a rotation transformation to the text that adds a nice touch to the overall effect.
If we apply a rotation transformation to the <text> to which we are applying the filter, the whole filter region will be rotated, including the image in the background:

This also happens if you apply other styles to the source text. For example, if you set the opacity on the <text> to 0.5, the text and the image in the background will also be affected by that.
In order to rotate the text but not the rest of the filter region, we can wrap the text in a group (<g>) and apply the filter to the group, and then apply the rotation transformation on the text. This will ensure that only the text is rotated, while the rest of the filter region, which is now defined by the group wrapper, remains unaffected by the transformation. This workaround is courtesy of Amelia Bellamy-Royds.
<g filter=”url(#conform)”>
<text dx=”60″ dy=”200″ font-size=”10em” transform=”translate(-20 30) rotate(-7)” fill=”#00826C”>organic</text>
</g>
I’ve tweaked the transformation a little to add a translation to make sure the text remains centered in the filter region. The result of this transformation now looks like this:

Note that I’m applying the rotation transformation to the text using the SVG transform attribute and not via CSS because, at the time of writing of this article, Internet Explorer and MSEdge don’t support CSS transformations on SVG elements.
Live Demo
This text displacement effect currently works in all major browsers, including MSEdge. The following is a screenshot of the effect in MSEdge:

This said, Chrome has recently stopped applying the distortion effect on the text. There’s some more information about this issue in this thread. The rest of the filter operations, however, work and are applied just fine, so, until Chrome fixes this issue, you should be able to see the text blended with the background, only without the distortion along its edges. The following is a screenshot of what the demo looks like in Chrome:

You can check the live demo out here.
Final words
I hope you’re starting to enjoy the power of SVG filters and thinking of more possibilities and effects to create with them already.
If you liked the idea of conforming text to surface texture, then you’re going to love learning how to create your own texture in SVG. Yup, you read that right. SVG can create texture. In the next article, we’re going to learn how to create a simple texture using a combination of SVG-generated noise and lighting effects. Stay tuned.
SVG Filter Effects: Conforming Text to Surface Texture with <feDisplacementMap> was written by Sara Soueidan and published on Codrops.

 Welcome back, Readers! It’s February, and I don’t think I have a single pink or chocolate-themed site anywhere in the mix. Ah well…
Welcome back, Readers! It’s February, and I don’t think I have a single pink or chocolate-themed site anywhere in the mix. Ah well… , kids. If you find an idea you like and want to adapt to your own site, remember to implement it responsibly.
, kids. If you find an idea you like and want to adapt to your own site, remember to implement it responsibly.













![]()
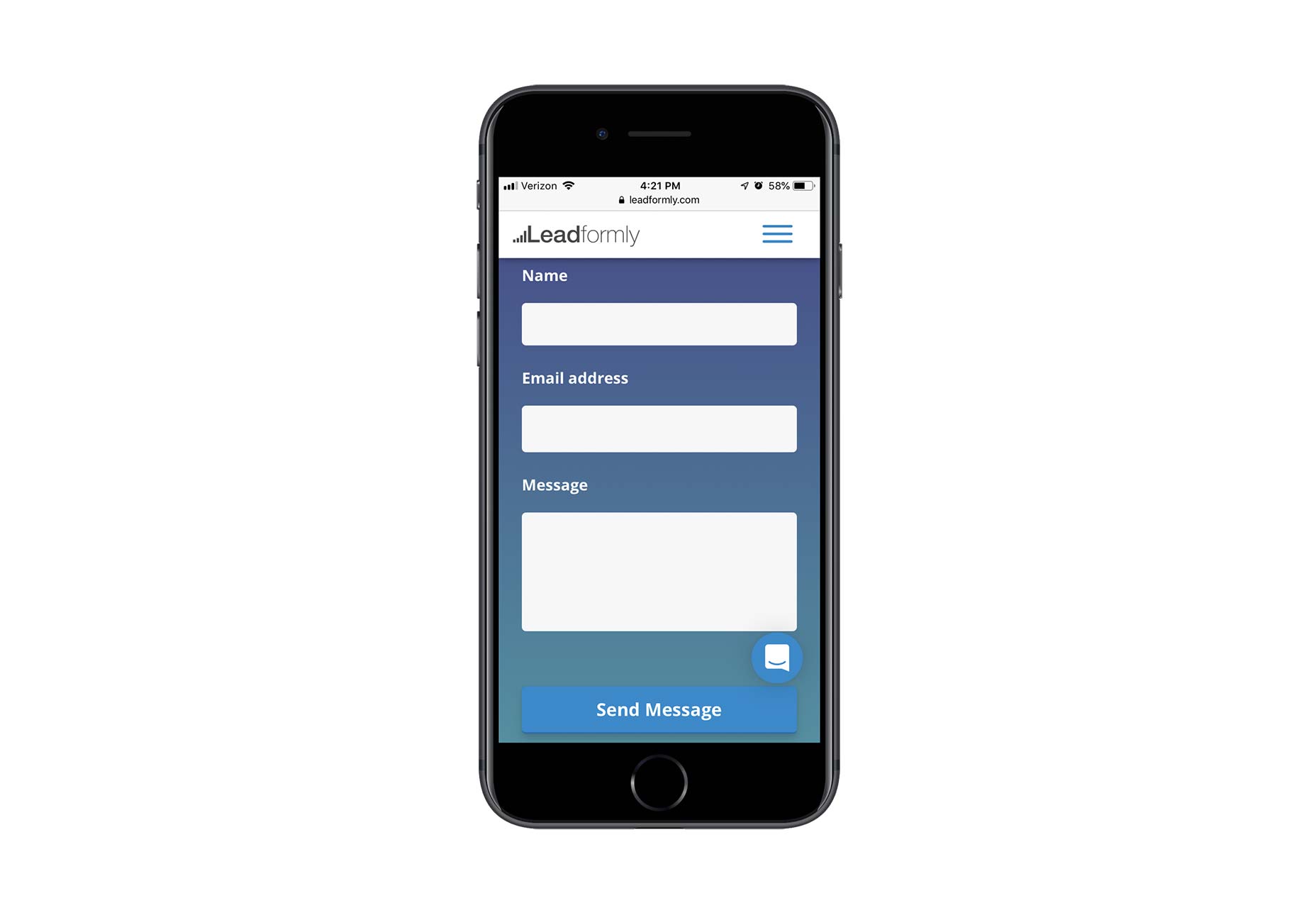
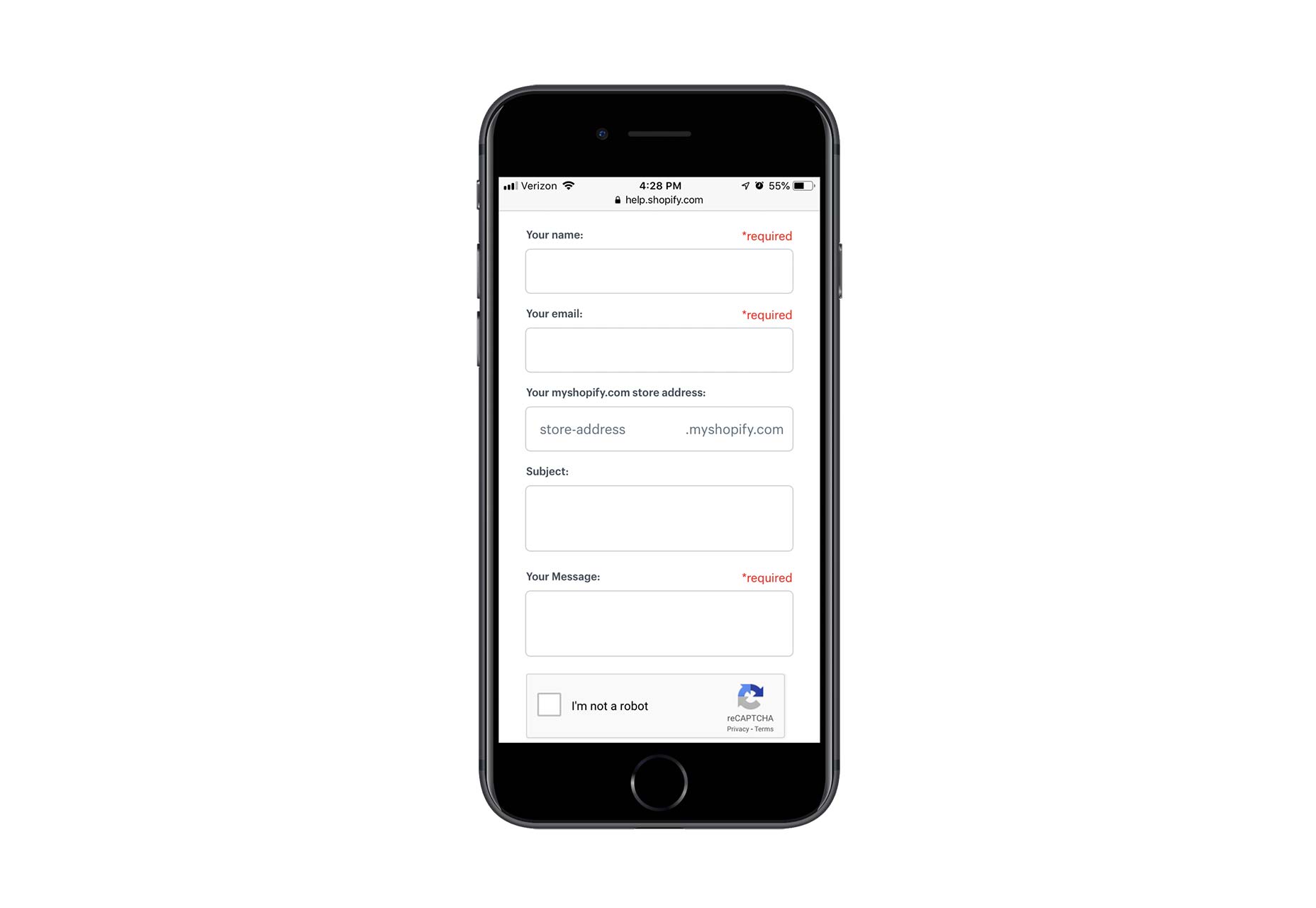
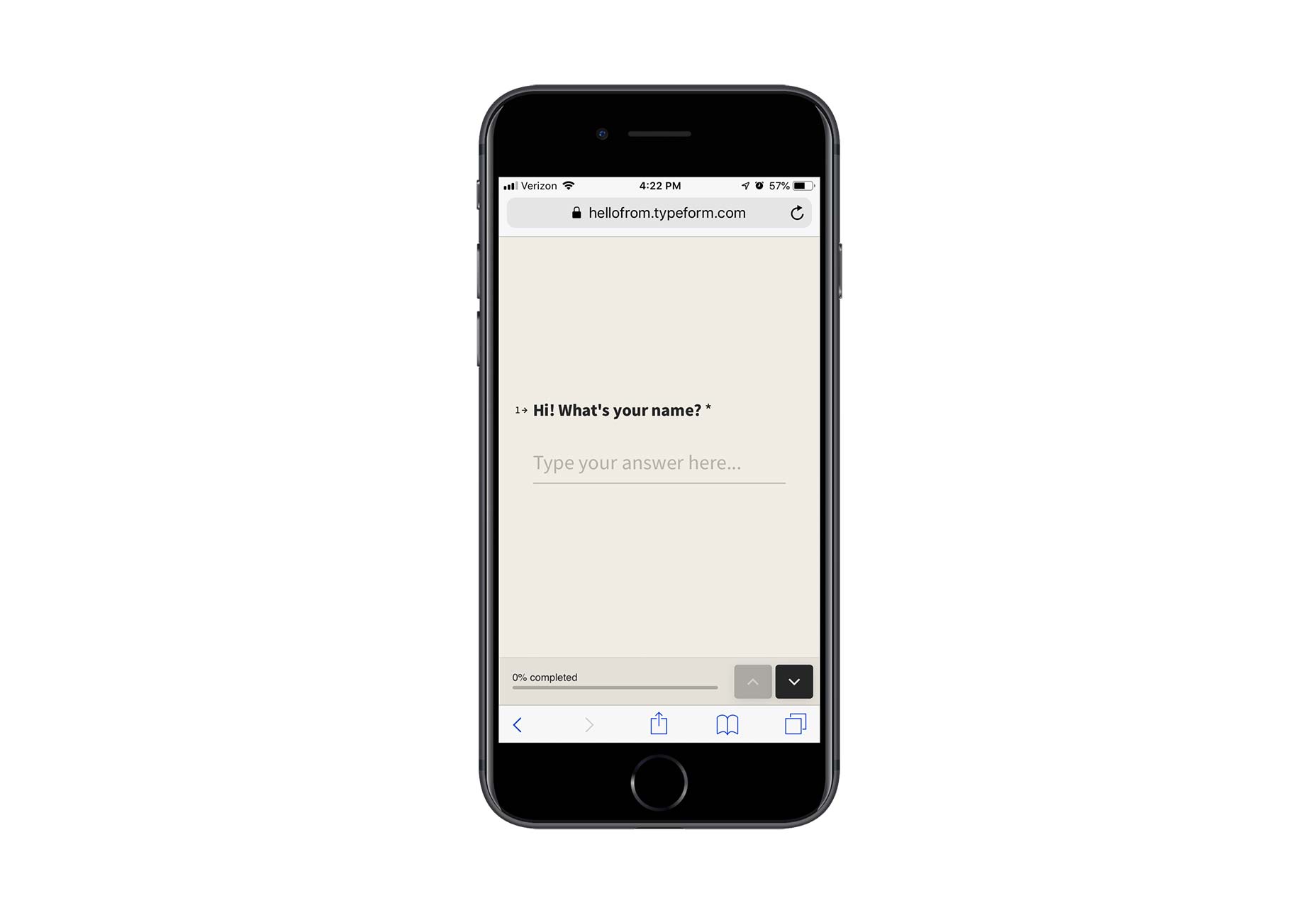
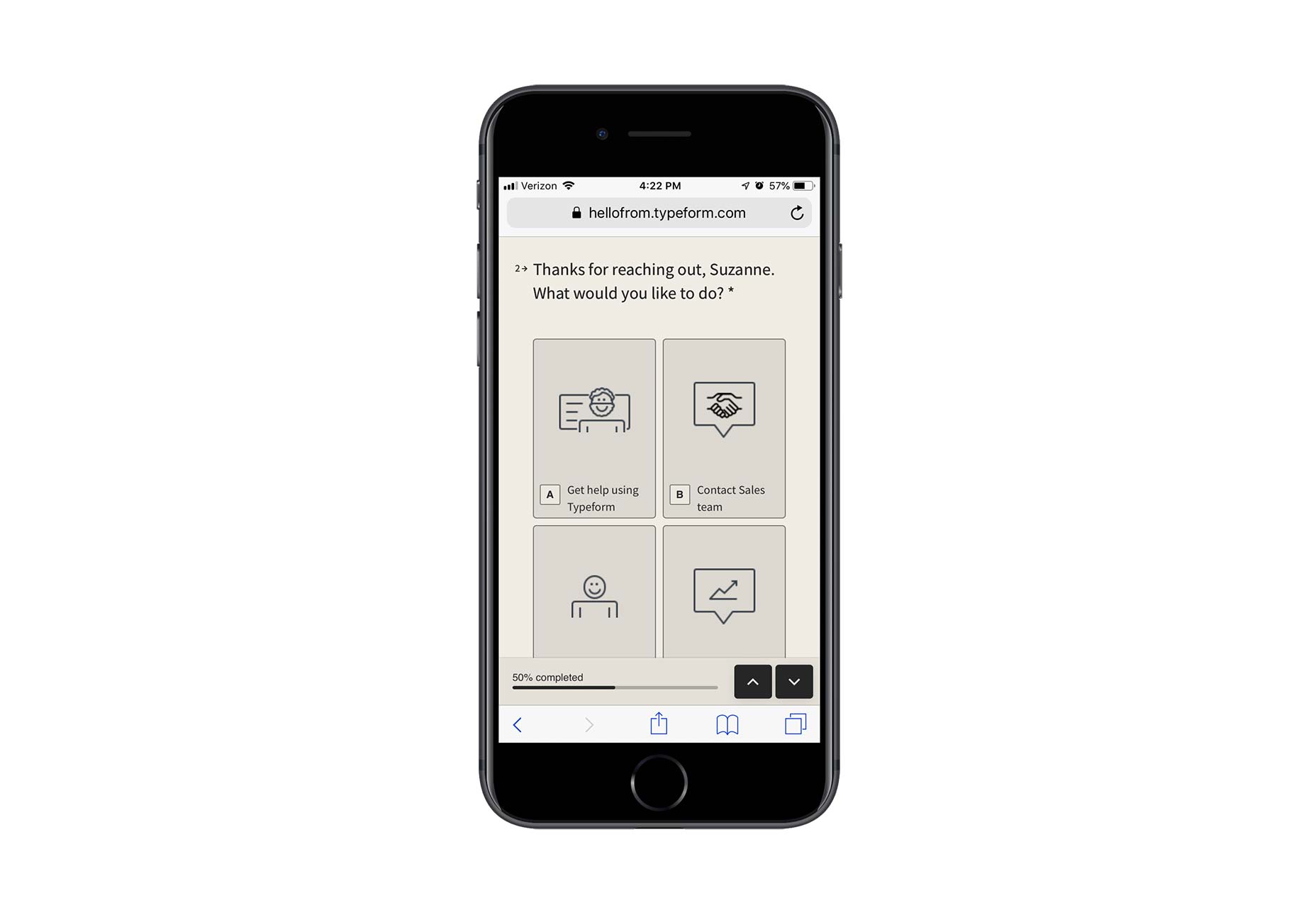
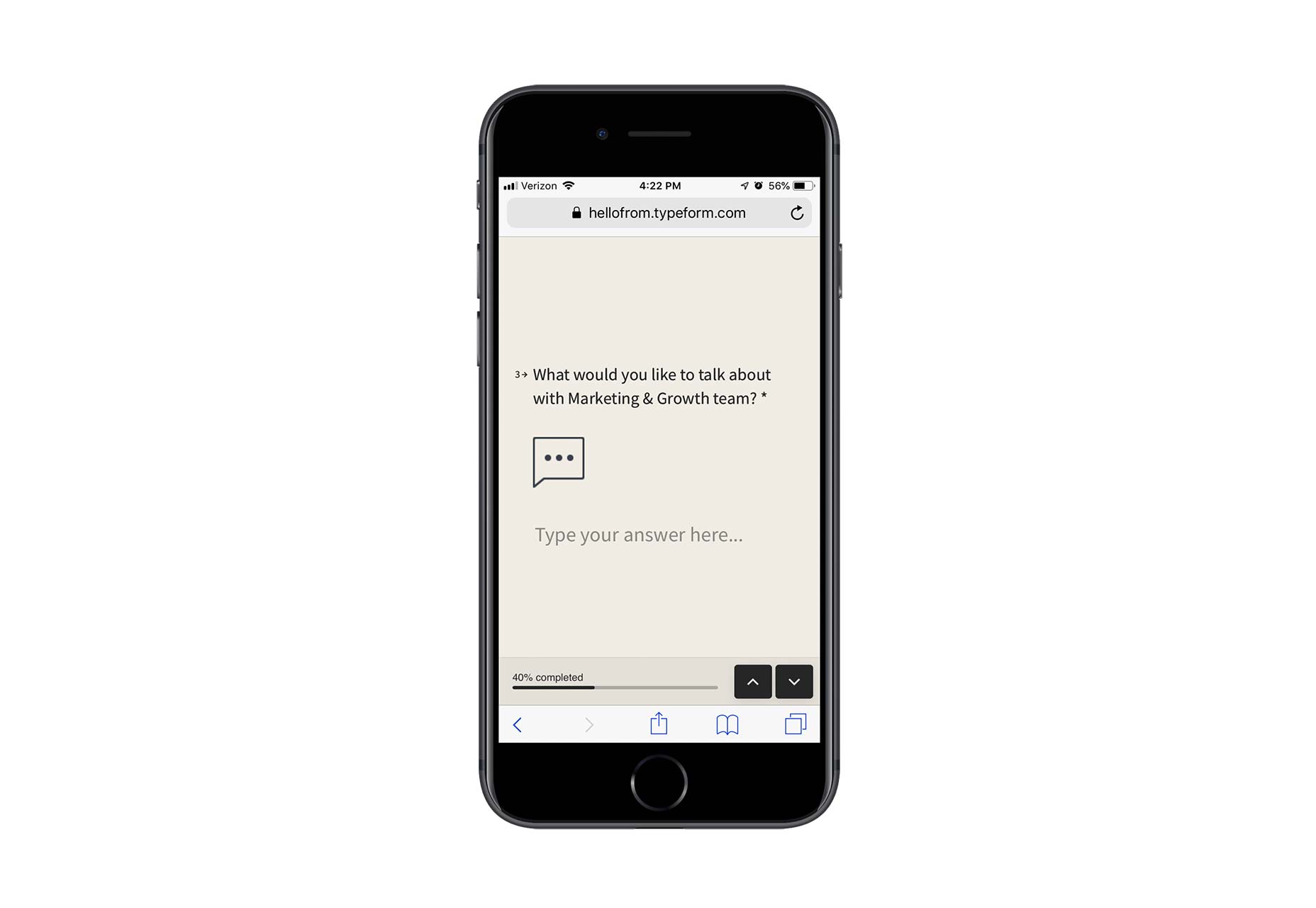
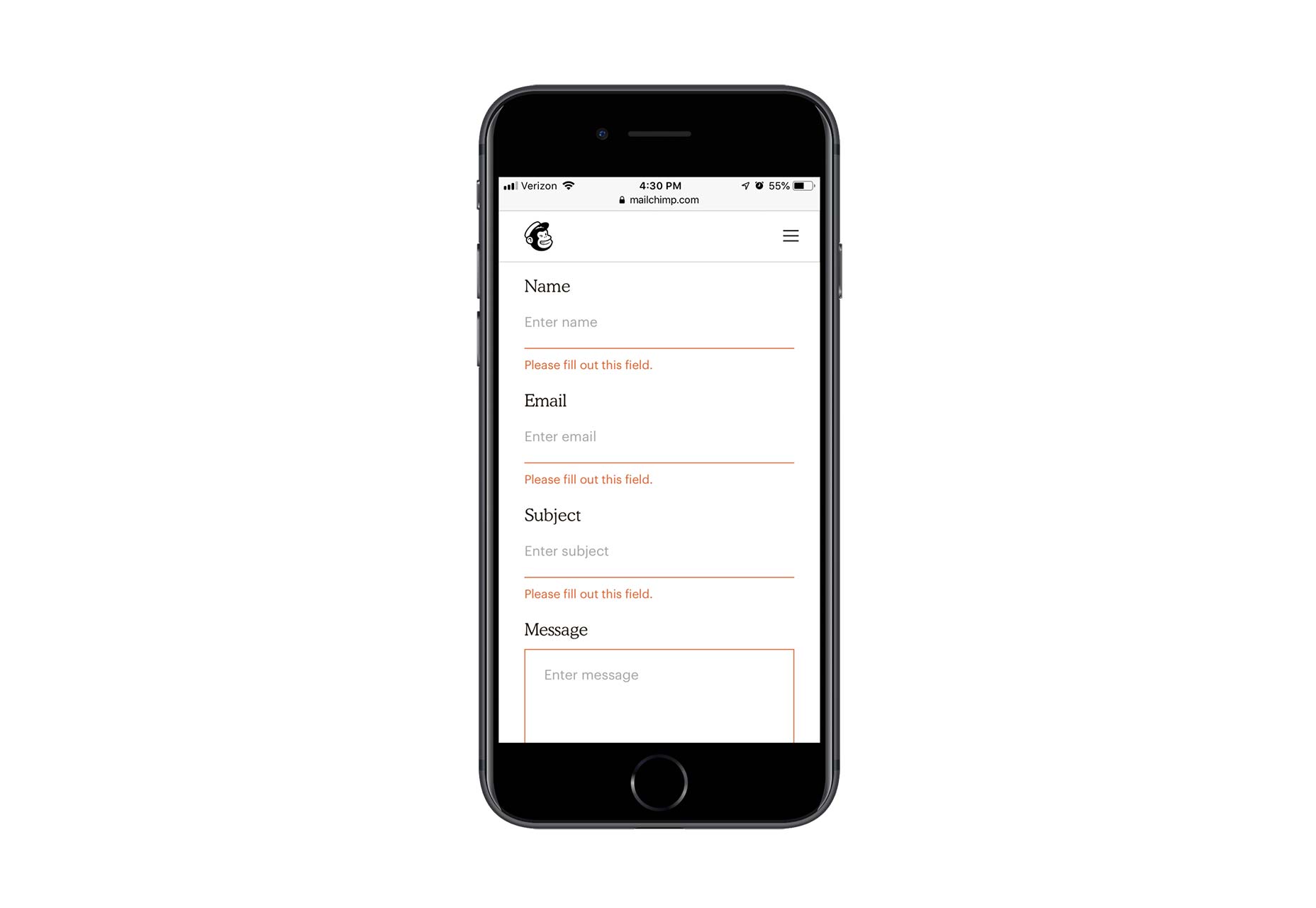
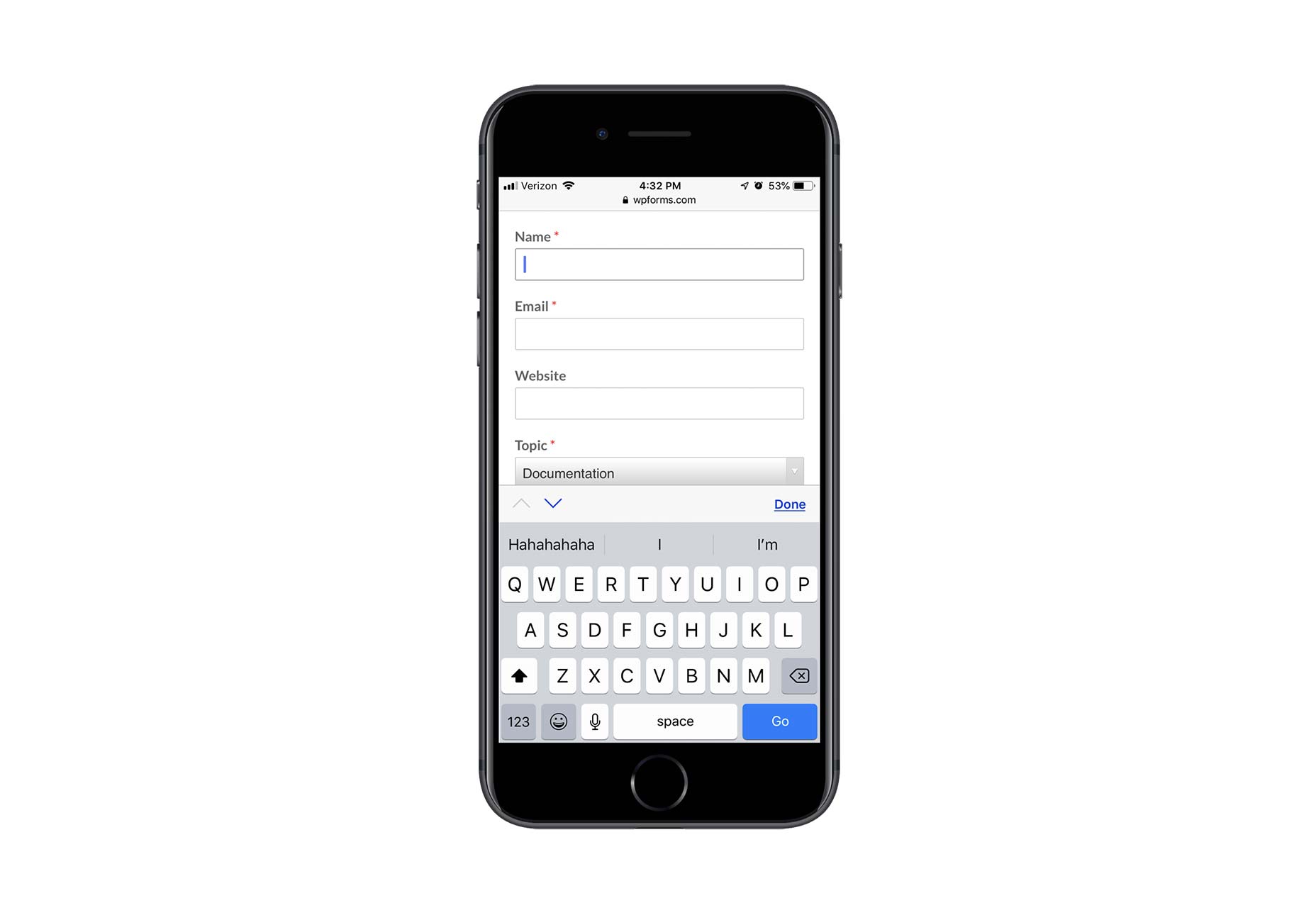
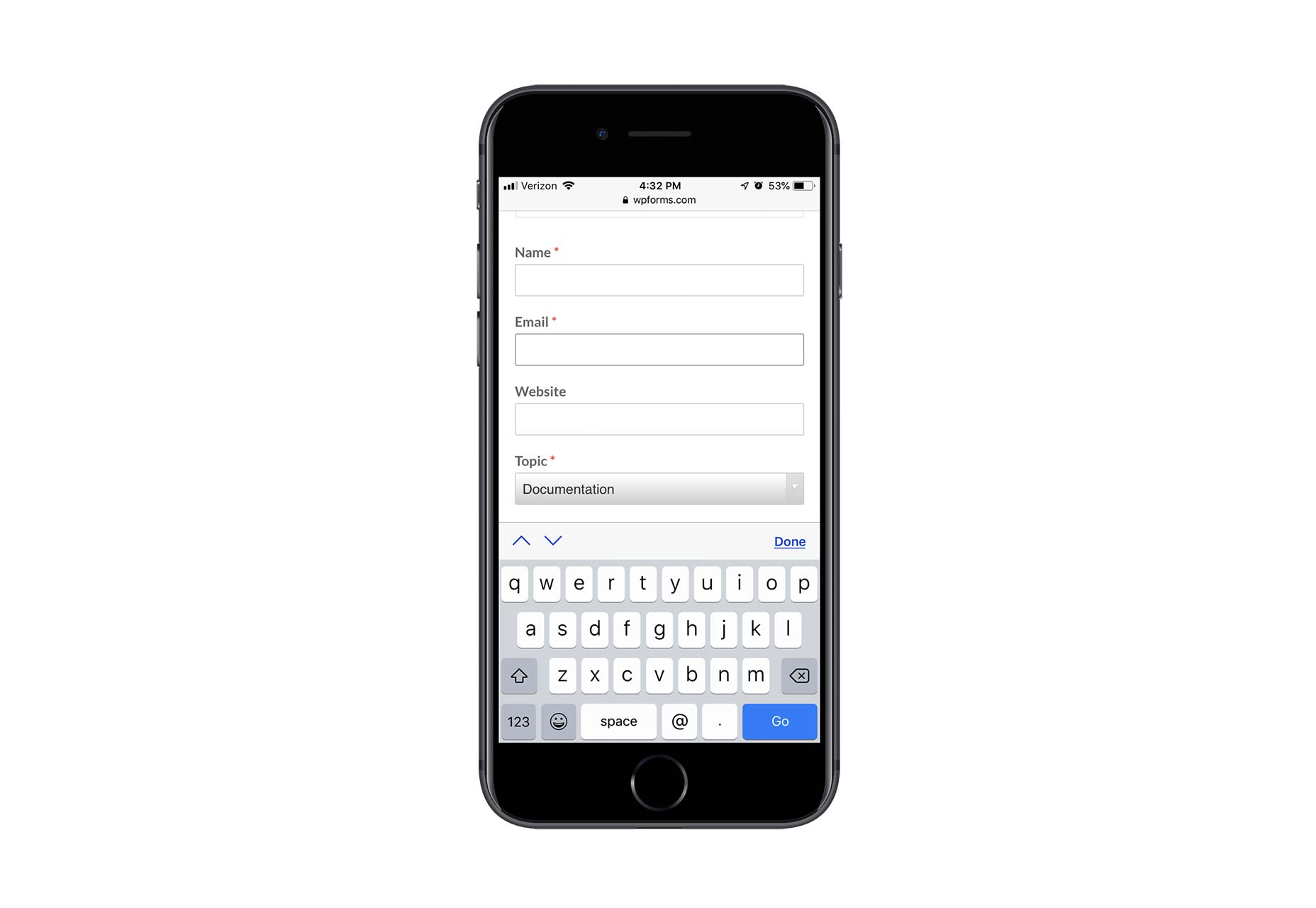
 Contact forms are a necessity for websites. Without them, your clients would be relegated to handling website- or business-related matters over the phone or email. Worse, they’d have absolutely no context for the call or message, which would increase the amount of time they’d have to spend responding to it.
Contact forms are a necessity for websites. Without them, your clients would be relegated to handling website- or business-related matters over the phone or email. Worse, they’d have absolutely no context for the call or message, which would increase the amount of time they’d have to spend responding to it.